It is well known that the main function of virus mRNA or mRNA is to translate virus protein as the template. However, in recent years, Prof. MENG Songdong’s research group in Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (IMCAS) found that the new function of virus is directly involved in the regulation of virus replication, infection and pathology as the competitive virus RNA (cvRNA). CvRNA is the new model of interaction between virus and host proposed by Prof. MENG’s research group.
They recently found that three RNAs of HBV (pgRNA, Pre-S and S mRNA) all had the binding sites of host miRNA let-7a, which absorbed and degraded let-7a in liver cells. Inhibition of let-7a resulted in an increase in its targets including c-myc, K-RAS and CCR7, which further promoted the occurrence and development of HCC. It will provide a clue for revealing the mechanism of chronic hepatitis B infection in hepatocellular carcinoma and the discovery of new targets for the treatment of HCC.
The research has been published online in Cancer Letter
(http://www.cancerletters.info/article/S0304-3835(16)30570-5/fulltext). Dr. DENG Mengmeng is the first author. LI Changfei and Prof. MENG Songdong are the corresponding authors. This is the third thesis studying competitive virus RNA. They have found that HBV RNA as the cvRNA was involved in promoting virus replication, enhancing viral adaptation to hepatocyte environment and inducing HCC. Research results have been published respectively in Journal of Virology (2013) and Scientific Reports (2015).
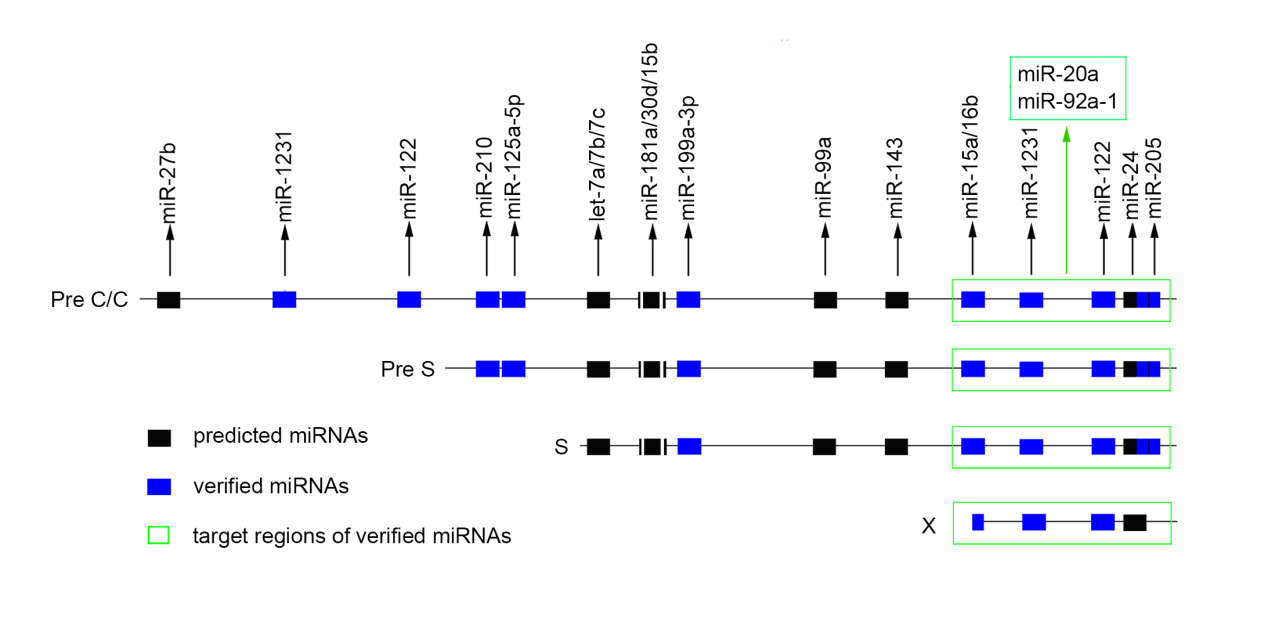
Figure: Binding sites for HBV pgRNA (Pre C/C), Pre S, S, X mRNA and miRNAs in liver cells (Image by Prof. MENG’s group)
